The U.S. Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) named Arturo Cardenas as the agency’s Director of Programs, the agency announced in a Sept. 24 release.
Cardenas oversees all operations to process and pay benefits administered by the agency. He will also serve on the RRB’s Executive Committee responsible for day-to-day operations of the agency and making policy recommendations to the three-member Board.
A career public servant, Mr. Cardenas worked at the Social Security Administration (SSA) for more than 30 years before joining RRB. During that time, he worked in a variety of positions in SSA field offices, regional offices and headquarters units.
His appointment was effective Aug. 30. He replaces Crystal Coleman, who retired in April 2021 after 29 years of federal service.
Tag: Railroad Retirement Board

Credit for a month of railroad service is earned for every month in which an employee had some compensated service covered by the Railroad Retirement Act. (Local lodge compensation is disregarded for any calendar month in which it is less than $25. However, work by a local lodge or division secretary collecting insurance premiums, regardless of the amount of salary, is creditable railroad work.) Also, under certain circumstances, additional service months may be deemed in some cases where an employee does not actually work in every month of the year.
The following questions and answers describe the conditions under which an employee may receive additional Railroad Retirement service month credits under the deeming provisions of the Railroad Retirement Act.
1. What requirements must be met before additional service months can be deemed?
A service month can be deemed if an employee has less than 12 service months reported in the year, has sufficient compensation reported and is in an “employment relation” with a covered railroad employer, or is an employee representative, during that month. (An employee representative is a labor official of a non-covered labor organization who represents employees covered under the acts administered by the Railroad Retirement Board.)
For this purpose, an “employment relation” generally exists for an employee on an approved leave of absence (for example, furlough, sick leave, suspension, etc.). An “employment relation” is severed by retirement, resignation, relinquishing job rights in order to receive a separation allowance or termination.
2. How is credit for additional service months computed?
For additional service months to be deemed, the employee’s compensation for the year, up to the annual Tier II maximum, must exceed an amount equal to 1/12 of the Tier II maximum multiplied by the number of service months actually worked. The excess amount is then divided by 1/12 of the Tier II maximum; the result, rounded up to the next whole number, equals the maximum number of months that may be deemed as service months for that year. Fewer months may be deemed, if an employment relation, as defined in Question 1, does not exist.
3. An employee works seven months in 2021 before being furloughed, but earns compensation of $108,000. How many deemed service months could be credited to the employee?
The employee could be credited with five additional service months. One-twelfth of the 2021 $106,200 Tier II maximum ($8,850) times the employee’s actual service months (seven) equals $61,950. The employee’s compensation in excess of $61,950 up to the $106,200 maximum is $44,250, which divided by $8,850 equals five. Therefore, five deemed service months could be added to the seven months actually worked and the employee would receive credit for 12 service months in 2021.
4. Another employee works for seven months in 2021 and earns compensation of $85,200. How many deemed service months could be credited to this employee?
In this case, the excess amount ($85,200 minus $61,950) is $23,250, which divided by $8,850 equals 2.627. After rounding, this employee could receive credit for three deemed service months and be credited with a total of 10 months of service in 2021.
5. Another employee works for eight months in 2021 before resigning on August 15, but earns compensation of $91,000. How many deemed service months could be credited to this employee?
None. Since the employee resigned in August, there is no employment relationship for the remaining months and no additional service months may be deemed and credited.
6. Should an employee preparing to retire take deemed service months into account when designating the date his or her Railroad Retirement annuity begins?
An employee may wish to consider credit for deemed service months in selecting an annuity beginning date. For instance, in some cases, a designated annuity beginning date that considers deemed service months could be used to establish basic eligibility for certain benefits, increase an annuity’s Tier II amount, or establish a current connection, as illustrated in Questions 7, 8 and 9, respectively. It should be noted that service months cannot be deemed after the annuity beginning date.
7. What would be an example of using deemed service months to establish benefit eligibility?
An example would be an employee between the ages of 60 and 62 who might be able to use deemed service months to establish the 360 months of service needed to qualify for an unreduced age annuity prior to full retirement age.
For instance, a 60-year-old employee last performed service on May 15, 2021, and received $61,800 in compensation in 2021. She is credited with 358 months of creditable railroad service through May 2021. If the employee wishes to retire on age, she must wait until she is full retirement age, which ranges between 66 and 67 depending upon the employee’s year of birth, or age 62 if she is willing to accept an age-reduced annuity. She needs at least two additional months of service to establish eligibility for an unreduced annuity prior to full retirement age.
The employee’s excess amount ($61,800 minus $44,250) is $17,550, which divided by $8,850 equals 1.983. Therefore, two deemed service months could be added to the five months actually worked and the employee would receive credit for seven service months in 2021 for a total of 360 service months, allowing her to receive an unreduced annuity beginning July 2, 2021.
8. How could deemed service months be used to increase an employee’s Tier II amount?
An employee worked in the first five months of 2021 and received compensation of $59,500. He does not relinquish his rights until July 2, 2021, and applies for an annuity to begin on that date.
The excess amount ($59,500 minus $44,250) is $15,250, which divided by $8,850 equals 1.723, which yields two deemed service months for a total of seven service months in 2021. Had the employee relinquished his rights and applied for an annuity to begin on July 1, he would have been given credit for only six service months.
The employee received the maximum compensation in all of the last five years and had 360 months of service through 2020. The additional service and compensation increases his Tier II from $1,726.75 to $1,746.92. However, delaying the annuity beginning date past the second day of the month after the date last worked solely to increase the Tier II amount would not generally be to the employee’s advantage.
9. Can deemed service months help an employee establish a current connection?
Yes. For example, an employee left the railroad industry in 2002 and engaged in employment covered by the Social Security Act. In August 2020, she returned to railroad employment and worked through June 28, 2021. She received compensation of $53,650 in 2021. She does not relinquish her rights until July 2, 2021, and applies for an annuity to begin on July 2, 2021.
In this case, the excess amount ($53,650 minus $53,100) is $550, which divided by $8,850 equals 0.0621, which yields one deemed service month. Consequently, the employee is given credit for seven service months in 2021. With five months of service in 2020 and seven months in 2021, the employee establishes a current connection. Had she designated the earliest annuity beginning date permitted by law, she would not have met the 12-in-30-month requirement for a current connection. (An employee who worked for a railroad in at least 12 months in the 30 months immediately preceding the month his or her Railroad Retirement annuity begins will meet the current connection requirement for a supplemental annuity, occupational disability annuity or survivor benefits.)
10. Can an employee ever receive credit for more than 12 service months in any calendar year?
No. Twelve service months are the maximum that can be credited for any calendar year.
11. Where can an employee get more information on how deemed service months could affect his or her annuity?
Employees with questions about deemed service months can send a secure message to their local RRB office by accessing Field Office Locator at RRB.gov and clicking on the link at the bottom of their local office’s page. If a customer needs to talk to an RRB employee, they can call the agency’s toll-free number (1-877-772-5772). However, customers are asked to be patient because of the increase in call volume due to the closure to the public of RRB offices during the COVID-19 pandemic.

The following questions and answers describe these benefits, their eligibility requirements and how to claim them. At the time this news release was issued, unemployment and sickness benefit flexibilities were in place due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Because these flexibilities are temporary and may change, they are not covered in this release. Visit RRB.gov/coronavirus for up-to-date information.
1. What are the eligibility requirements for railroad unemployment and sickness benefits in July 2021?
To qualify for normal railroad unemployment or sickness benefits, an employee must have had railroad earnings of at least $4,137.50 in calendar year 2020, counting no more than $1,655 for any one month. Those who were first employed in the rail industry in 2020 must also have at least five months of creditable railroad service in 2020.
Under certain conditions, employees who do not qualify on the basis of their 2020 earnings may still be able to receive benefits in the new benefit year. Employees with at least 10 years of service (120 or more months of service) who received normal benefits in the benefit year ending June 30, 2021, may be eligible for extended benefits. Employees with at least 10 years of service (120 or more months of service) might qualify for accelerated benefits if they have railroad earnings of at least $4,275 in 2021, not counting earnings of more than $1,710 in any one month.
In order to qualify for extended unemployment benefits, a claimant must not have voluntarily quit work without good cause and not have voluntarily retired. To qualify for extended sickness benefits, a claimant must not have voluntarily retired and must be under age 65.
To be eligible for accelerated benefits, a claimant must have 14 or more consecutive days of unemployment or sickness; not have voluntarily retired or, if claiming unemployment benefits, quit work without good cause; and, when claiming sickness benefits, be under age 65.
2. What is the daily benefit rate payable in the new benefit year beginning July 1, 2021?
Almost all employees will qualify for the maximum daily benefit rate of $82. Benefits are generally payable for the number of days of unemployment or sickness over four in 14-day claim periods, which yields $820 for each two full weeks of unemployment or sickness. Sickness benefits payable for the first 6 months after the month the employee last worked are subject to Tier I Railroad Retirement payroll taxes, unless benefits are being paid for an on-the-job injury.
Claimants should be aware that as a result of a sequestration order under the Budget Control Act of 2011, the RRB will reduce unemployment and sickness benefits by 5.7% through September 30, 2021. Consequently, the total maximum amount payable in a 2-week period covering 10 days of unemployment or sickness will be $773.26. The maximum amount payable for sickness benefits subject to Tier I payroll taxes of 7.65% will be $714.11 over two weeks. Future reductions, should they occur, will be calculated based on applicable law.
(The temporary benefits created under the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, Continued Assistance to Rail Workers Act of 2020 (CARWA), and American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 are not subject to sequestration. Under CARWA, beginning January 3, 2021, all benefits under the RUIA (including normal unemployment and sickness benefits as well as normal extended unemployment and sickness benefits) will be exempt from sequestration until 30 days after the Presidential declaration of a national emergency concerning COVID-19 terminates. The RRB will publish updated information regarding the status of the sequestration of RUIA benefits when the end date of the Presidential declaration of a national emergency is known.)
3. How long are these benefits payable?
Normal unemployment or sickness benefits are each payable for up to 130 days (26 weeks) in a benefit year. The total amount of each kind of benefit which may be paid in the new benefit year cannot exceed the employee’s railroad earnings in calendar year 2020, counting earnings up to $2,138 per month.
If normal benefits are exhausted, extended benefits are payable for up to 65 days (during seven consecutive 14-day claim periods) to employees with at least 10 years of service (120 or more cumulative service months).
4. What is the waiting period requirement for unemployment and sickness benefits?
There is a seven-day waiting period requirement, prior to any benefits becoming payable under the RUIA. During the first 14-day claim period, benefits are payable for every day claimed in excess of seven days. Subsequent claims are paid for the number of days of unemployment or sickness over four in each 14-day registration period. Initial sickness claims must also begin with four consecutive days of sickness. If an employee has at least five days of unemployment or five days of sickness in a 14-day period, he or she should still file for benefits in order to satisfy the waiting period for the current benefit year. Separate waiting periods are required for unemployment and sickness benefits. However, only one seven-day waiting period is generally required during any period of continuing unemployment or sickness, even if that period continues into a subsequent benefit year.
5. Are there special waiting period requirements if unemployment is due to a strike?
If a worker is unemployed because of a strike conducted in accordance with the Railway Labor Act, benefits are not payable for days of unemployment during the first 14 days of the strike, but benefits are payable during subsequent 14-day periods.
If a strike is in violation of the Railway Labor Act, unemployment benefits are not payable to employees participating in the strike. However, employees not among those participating in such an illegal strike, but who are unemployed on account of the strike, may receive benefits after the first two weeks of the strike.
While a benefit year waiting period cannot count toward a strike waiting period, the 14-day strike waiting period may count as the benefit year waiting period if a worker subsequently becomes unemployed for reasons other than a strike later in the benefit year.
6. Can employees in train and engine service receive unemployment benefits for days when they are standing by or laying over between scheduled runs?
No, not if they are standing by or laying over between regularly assigned trips or they missed a turn in pool service.
7. Can extra-board employees receive unemployment benefits between jobs?
Yes, but only if the miles and/or hours they actually worked were less than the equivalent of normal full-time work in their class of service during the 14-day claim period. Entitlement to benefits would also depend on the employee’s earnings.
8. How would an employee’s earnings in a claim period affect his or her eligibility for unemployment benefits?
If a claimant’s earnings for days worked, and/or days of vacation, paid leave or other leave in a 14-day registration period are more than a certain indexed amount, no benefits are payable for any days of unemployment in that period. That registration period, however, can be used to satisfy the waiting period.
Earnings include pay from railroad and non-railroad work, as well as part-time work and self-employment. Earnings also include pay that an employee would have earned except for failure to mark up or report for duty on time, or because he or she missed a turn in pool service or was otherwise not ready or willing to work. For the benefit year that begins July 2021, earnings of $1,655 or more in a claim period will disqualify a claim for unemployment benefits, even if there are more than 4 days of unemployment claimed. This amount corresponds to the base year monthly compensation amount used in determining eligibility for benefits in each year. Also, even if an earnings test applies on the first claim in a benefit year, this will not prevent the first claim from satisfying the waiting period in a benefit year.
Earnings of $15 or less per day from work which is substantially less than full-time and not inconsistent with the holding of normal full-time employment may be considered subsidiary remuneration and may not prevent payment of any days in a claim. However, a claimant must report all full and part-time work on each claim, regardless of the amount of earnings, so the RRB can determine if the work affects benefits.
9. How does a person apply for and claim unemployment benefits?
Employees can apply for and claim unemployment benefits online or by mail. Individuals who have established an account through myRRB at RRB.gov can log in and file their applications and their biweekly claims online. Employees who need to create an account should visit RRB.gov/myRRB and click on the button labeled Sign in with login.gov. Employees are encouraged to establish their accounts while still working to expedite the filing process for future unemployment benefits, and for access to other online services.
To apply by mail, claimants must obtain an Application for Unemployment Benefits (Form UI-1) from RRB.gov, their labor organization or railroad employer. The completed application should be mailed to the local RRB office as soon as possible and must be filed within 30 days from the date the claimant became unemployed, or the first day for which he or she wishes to claim benefits. Benefits may be lost if the application is filed late. Claimants filing a late unemployment application or claim should include a signed statement explaining why they are unable to meet the required time frame.
Persons can find the address of the RRB office serving his or her area by visiting RRB.gov and clicking on Field Office Locator, or by calling the agency toll-free at 1-877-772-5772 and selecting the appropriate option from the automated menu.
The local RRB field office reviews the completed application, whether it was submitted online or by mail, and notifies the claimant’s current railroad employer, and base-year employer, if different. The employer has the right to provide information about the benefit application.
After processing the application, biweekly claim forms are provided to the claimant for as long as he or she remains unemployed and eligible for benefits. If a claimant filed an online application, his or her claim forms are only made available online. If a claimant filed a paper application, his or her first claim form is both available online and mailed to him or her. If the claimant returns the paper claim, future claims will be mailed to him or her. If the claimant files the claim online, all subsequent claim forms will only be made available online, and will no longer be mailed. Claimants must not file both an online and a paper claim form for the same period(s). Claim forms should be signed and sent (online or by mail) on or after the last day of the claim. The completed claim must be received by the RRB within 15 days of the end of the claim period, or within 15 days of the date the claim form was made available online or mailed to the claimant, whichever is later.
Only one application needs to be filed during a benefit year, even if a claimant becomes unemployed more than once. However, in the case of multiple claim periods, a claimant must request a claim form from the RRB within 30 days of the first day for which he or she wants to resume claiming benefits. These claim forms may then be filed online or by mail.
10. How does a person apply for and claim sickness benefits?
An Application for Sickness Benefits (Form SI-1a) can be obtained from RRB.gov, a railroad labor organization, or a railroad employer. Applications for sickness benefits must be submitted to the agency by mail. However, subsequent claims may be mailed, or completed online by employees who have established a myRRB account at RRB.gov.
An application including a doctor’s Statement of Sickness (Form SI-1b – included with form SI-1a) is required at the beginning of each period of continuing sickness for which benefits are claimed. Claimants should make a special effort to have the doctor’s statement of sickness completed promptly since claims cannot be paid without it.
The RRB suggests that employees keep an application for sickness benefits on hand, and that family members know where the form is kept and how to use it. If an employee becomes unable to work because of sickness or injury, the employee should complete the application and have his or her doctor complete the attached statement of sickness. If a claimant receives sickness benefits for an injury or illness for which he or she is paid damages, it is important to be aware that the RRB is entitled to reimbursement of either the amount of the benefits paid for the injury or illness or the net amount of the settlement, after deducting the claimant’s gross medical, hospital and legal expenses, whichever is less.
If the employee is too sick to complete the application, someone else may complete it for him or her. In such cases, a family member should also complete a Statement of Authority to Act for Employee (Form SI-10 included with form SI-1a), which accompanies the statement of sickness.
After completion, the forms should be mailed to the RRB’s headquarters in Chicago within 10 days from when the employee became sick or injured. However, applications received after 10 days but within 30 days of the first day for which an employee wishes to claim benefits are generally considered timely filed if there is a good reason for the delay. (Employees cannot currently file their sickness applications online.) Upon receipt, the RRB will process the application and determine if the employee is eligible for sickness benefits.
After processing the application and statement of sickness, the RRB makes the first biweekly claim form available online (for employees with myRRB accounts) and mails a paper form to the employee as long as he or she is eligible for benefits and remains unable to work due to illness or injury. Those choosing to file the paper claim received by mail should return the completed form to RRB headquarters for processing. If the claimant returns the paper claim, future claims will be mailed to him or her. If the claimant files the claim online, all subsequent claim forms will only be made available online, and will no longer be mailed. Claimants must not file both online and paper claim forms for the same claim period(s). Employees who need to create a myRRB account should visit RRB.gov/myRRB and click on the button labeled Sign in with login.gov.
Completed claim forms must be received at the RRB within 30 days of the last day of the claim period, or within 30 days of the date the claim form was made available online or mailed to the claimant, whichever is later. Benefits may be lost if an application or claim form is filed late. Claimants filing a late sickness application or claim form should include a signed statement explaining why they were unable to meet the required time frame.
Claimants are reminded that while claim forms for sickness benefits can be submitted online, applications for sickness benefits must be mailed to the RRB. Statements of sickness may be mailed with the sickness application or faxed directly from the doctor’s office to the RRB at 312-751-7185. Faxes must include a cover sheet from the doctor’s office. Also, in order to prevent a delay in processing applications or claims, employees are advised against sending any sickness benefit forms to the RRB in Chicago via certified mail.
11. Is a claimant’s employer notified each time a biweekly claim for unemployment or sickness benefits is filed?
The RUIA requires the RRB to notify the claimant’s base-year employer each time a claim for benefits is filed. That employer has the right to submit information relevant to the claim before the RRB makes an initial determination on the claim. Benefits may not be paid at this time but the employee will receive a notice and have the right to appeal. In addition, if a claimant’s base-year employer is not his or her current employer, the claimant’s current employer is also notified. The RRB must also notify the claimant’s base-year employer each time benefits are paid to a claimant. The base-year employer may protest the decision to pay benefits. Such a protest does not prevent the timely payment of benefits. However, a claimant may be required to repay benefits if the employer’s protest is ultimately successful. The employer also has the right to appeal an unfavorable decision to the RRB’s Bureau of Hearings and Appeals.
The RRB also conducts checks with other Ffederal agencies and all 50 states, as well as the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico, to detect fraudulent benefit claims, and it checks with physicians to verify the accuracy of medical statements supporting sickness benefit claims.
12. How long does it take to receive payment?
Under the RRB’s Customer Service Plan, if a claimant files an application for unemployment or sickness benefits, the RRB will release a claim form or a denial letter within 10 days of receiving his or her application. If a claim for subsequent biweekly unemployment or sickness benefits is filed, the RRB will certify a payment or release a denial letter within 10 days of the date the RRB receives the claim form. If the claimant is entitled to benefits, his or her benefits will generally be paid within one week of that decision.
If a claimant does not receive a decision notice or payment within the specified time period, he or she may expect an explanation for the delay and an estimate of the time required to make a decision.
However, some claims for benefits may take longer to handle than others, especially if they are more complex, or if an RRB office has to get information from other people or organizations, or under special circumstances such as the current pandemic.
Claimants who think an RRB office made the wrong decision about their benefits have the right to ask for review and to appeal. They will be notified of these rights each time an unfavorable decision is made on their claims.
13. How are payments made?
Railroad unemployment and sickness insurance benefits are paid by direct deposit to an employee’s bank, savings and loan, credit union or other financial institution. New applicants for unemployment and sickness benefits will be asked to provide information needed for direct deposit enrollment.
14. How can claimants get more information on their railroad unemployment or sickness claims?
Claimants with myRRB accounts can view their individual railroad unemployment and sickness insurance account statement by using the View RUIA Account service. This statement displays the type and amount of the claimant’s last five benefit payments, the claim period for which the payments were made, and the dates that the payments were approved. Individuals can also confirm the RRB’s receipt of applications and claims.
In addition, claimants can call the agency toll-free at 1-877-772-5772 to access information about the status of unemployment and sickness claims or payments 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Individuals with questions about unemployment or sickness benefits, or who need information about their specific claims and benefit payments, can send a secure e-mail to their local office by accessing the Field Office Locator at RRB.gov and clicking on the link at the bottom of their local office’s page. If a customer needs to talk to an RRB employee, they can call the agency’s toll-free number (1-877-772-5772). However, customers are asked to be patient because of the increase in call volume due to the closure to the public of RRB offices during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) Labor Member John Bragg announced June 17 that Assistant to the Labor Member Geraldine “Geri” Clark will be retiring July 2 after 51 years with the agency.
“Geri’s retirement is a great loss to my office and the RRB. Her 51 years of dedication to the RRB, rail labor, and to both active and retired rail workers is unmatched. Her self-motivation, commitment to improving customer service and willingness to always go the extra mile when called upon will be greatly missed,” Bragg wrote in a letter announcing Clark’s retirement. “I wish Geri the best as she begins this new chapter in life, but most importantly I want to thank her for her service. She has truly been a pleasure to work with.”
Clark began working at RRB in 1970 and was appointed to her current position in 1985 by former Labor Member of the Board C. J. Chamberlain, becoming the first woman to be named a board assistant in the agency’s history. Geri also served as an assistant to succeeding Labor Members V.M. “Butch” Speakman, Jr. and W.A. “Walt” Barrows.
“Geri’s leaving will mark the end of an era for the Railroad Retirement Board, and I am indebted to her dedication and commitment to the men and women of the rail industry who keep this country moving,” Bragg wrote. “Her work over the last 51 years has helped assure that railroad workers always receive the benefits they need and deserve.”
During her time in the Office of the Labor Member, Clark was the driving force behind the Informational Conference program. The conferences were introduced by the Labor Member to help educate local rail labor representatives about the benefits available to members and their families under the Railroad Retirement and Railroad Unemployment Insurance Acts. Thousands of representatives attended conferences over the years and achieved a better understanding of the provisions and financing of the Railroad Retirement and unemployment insurance systems, and of the administrative organization of the RRB. In turn, they helped improve the effectiveness of the agency’s benefit program operations by passing on to their fellow railroad employees the information they acquired at the conferences.
She was a frequent guest at numerous UTU/SMART-TD Regional Meetings, sharing her knowledge of the RRB to members on the cusp of retirement or who were just planning ahead.
More recently Clark spearheaded RRB’s Pre-Retirement Seminar program for workers. The seminars have proven to be a popular successor to the informational conferences, offering similar content, but open to rail labor representatives and also railroad employees and their spouses nearing retirement.
The leadership and the whole of SMART Transportation Division thank Geri Clark for her many decades of excellent service in helping to ensure that union members understand and get the RRB benefits to which they are entitled. We wish her a long, happy and healthy retirement!
The 2022 fiscal year budget proposed by the Biden administration May 28 offers a net increase in funding to the Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) to cover accumulating administrative costs and to improve customer service.

In its budget request to U.S. House leadership and to Vice President Kamala Harris, RRB reported that it has a staffing deficit of 12% from its minimum levels and that the RRB’s programs office has been operating at a reduced capacity because funding for the agency has been nearly flat for five years. Its workforce also is aging, with nearly a quarter of its workers now eligible to retire and 231 employees eligible to retire in the next year.
The added funding will allow RRB to increase its ranks to 801 full-time employees at a time when it needs workers to take care of retirement, survivor claims and numerous other customer-facing duties that had been hampered by the COVID-19 pandemic and chronic understaffing. In its budget request, RRB reported that just 35% of the 1.2 to 1.3 million calls its Bureau of Field Services received were answered in FY2020.
“We are operating in a transitional state that requires a sufficient investment in staffing to sustain benefit determination and payment operations, which still rely heavily on manual processing, while ensuring that the agency retains the knowledge of our laws and systems critical to modernizing benefit payment systems,” the agency stated. “The RRB believes that an increase in staffing is critical to the success of the agency over the next few years.”
The budget request is not the only way the current administration is working to improve RRB.
The agency’s years-long project to upgrade its IT infrastructure finally received full funding through Biden and Congress’s American Rescue Plan. The agency said that the modernization of RRB’s systems should also help to open the door to better service and more efficiency once fully implemented.
“We are grateful to the Congress for providing annual and supplemental appropriations that have fully funded RRB’s IT Modernization program,” RRB stated.
Read the RRB’s budget request and its 2022 Fiscal Year performance plan.

The following questions and answers describe the survivor benefits payable by the Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) and the eligibility requirements for these benefits.
- What are the general service requirements for Railroad Retirement survivor benefits?
With the exception of one type of lump-sum death benefit, eligibility for survivor benefits depends on whether or not a deceased employee was “insured” under the Railroad Retirement Act. An employee is insured if he or she has at least 120 months (10 years) of railroad service, or 60 months (5 years) performed after 1995, and a “current connection” with the railroad industry as of the month the annuity begins or the month of death, whichever occurs first.
- How is a “current connection” determined under the Railroad Retirement Act?
Generally, an employee who worked for a railroad in at least 12 months in the 30 months immediately preceding the month his or her Railroad Retirement annuity begins will meet the current connection requirement. If an employee dies before retirement, railroad service in at least 12 months in the 30 months before the month of death will meet the current connection requirement for the purpose of paying survivor benefits.
If an employee does not qualify on this basis, but has 12 months of service in an earlier 30-month period, he or she may still meet the current connection requirement. This alternative generally applies if the employee did not have any regular employment outside the railroad industry after the end of the last 30-month period which included 12 months of railroad service and before the month the annuity begins or the month of death, if earlier.
Full- or part-time work for a nonrailroad employer in the interval between the end of the last 30-month period including 12 months of railroad service and the beginning date of an employee’s annuity or the month of death, if earlier, can break a current connection.
Self-employment in an unincorporated business will not break a current connection; however, self-employment can break a current connection if the business is incorporated. All self-employment will be reviewed to determine if it meets the RRA’s standards for maintaining a current connection.
Working for certain U.S. government agencies — Department of Transportation, National Transportation Safety Board, Surface Transportation Board, Transportation Security Administration, National Mediation Board or the Railroad Retirement Board — will not break a current connection. State employment with the Alaska Railroad, so long as that railroad remains an entity of the State of Alaska, will not break a current connection. Also, railroad service in Canada for a Canadian railroad will neither break nor preserve a current connection.
A current connection can also be maintained, for purposes of survivor annuities, if the employee completed 25 years of railroad service, was involuntarily terminated without fault from his or her last job in the rail industry, and did not thereafter decline an offer of employment in the same class or craft in the rail industry, regardless of the distance to the new position.
A current connection determination is made when an employee files for a Railroad Retirement annuity. If an employee dies before applying for an annuity, it is made when an applicant files for a survivor annuity. Once a current connection is established at the time the Railroad Retirement annuity begins, an employee never loses it no matter what kind of work is performed thereafter.
- What if these service requirements are not met?
If a deceased employee did not have an insured status, jurisdiction of any survivor benefits payable is transferred to the Social Security Administration and survivor benefits are paid by that agency instead of the RRB. Regardless of which agency has jurisdiction, the deceased employee’s Railroad Retirement and Social Security credits will be combined for benefit computation purposes.
- What are the age and other eligibility requirements for widow(er)s who haven’t remarried?
Widow(er)s’ benefits are payable at age 60 or over. They are also payable at any age if the widow(er) is caring for an unmarried child of the deceased employee under age 18 or a disabled child of any age who became permanently disabled before age 22. Widow(er)s’ benefits are also payable at ages 50-59 if the widow(er) is totally disabled and unable to work in any regular employment. The disability must have begun within seven years after the employee’s death or within seven years after the termination of an annuity based on caring for a child of the deceased employee. In most cases, a five-month waiting period is required after the onset of disability before disability payments can begin.
Generally, the widow(er) must have been married to the employee for at least nine months prior to death, unless she or he was the natural or adoptive parent of their child, the employee’s death was accidental or while on active duty in the U.S. Armed Forces, the widow(er) was potentially entitled to certain Railroad Retirement or Social Security benefits in the month before the month of marriage, or the marriage was postponed due to state restrictions on the employee’s prior marriage and divorce due to mental incompetence or similar incapacity.
- Can surviving divorced spouses and remarried widow(er)s also qualify for benefits?
Survivor benefits may be payable to a surviving divorced spouse or remarried widow(er). Benefits are limited to the amount Social Security would pay (Tier I only) and therefore are less than the amount of the survivor annuity otherwise payable (Tier I and Tier II) by the RRB. A Tier II benefit is not provided for a surviving divorced spouse or a remarried widow(er).
A surviving divorced spouse may qualify if she or he was married to the employee for at least 10 years immediately before the date the divorce became final, and is age 60 or older (age 50 or older if disabled). A surviving divorced spouse who is unmarried can qualify at any age if caring for the employee’s child and the child is under age 16 or disabled, in which case the 10-year marriage requirement does not apply.
A widow(er) or surviving divorced spouse who remarries after age 60, or a disabled widow(er) or disabled surviving divorced spouse who remarries after age 50 may also receive the portion of a survivor annuity equivalent to a Social Security benefit (Tier I); however, remarriage prior to age 60 (or age 50 if disabled) would not prevent eligibility if that remarriage ended. Such Social Security level benefits may also be paid to a younger widow(er) or surviving divorced spouse caring for the employee’s child who is under age 16 or disabled, if the remarriage is to a person entitled to Railroad Retirement or Social Security benefits, or the remarriage ends.
- When are survivor benefits payable to children and other dependents?
Monthly survivor benefits are payable to an unmarried child under age 18, and to an unmarried child age 18 in full-time attendance at an elementary or secondary school, or in approved homeschooling, until the student attains age 19 or the end of the school term in progress when the student attains age 19. In most cases where a student attains age 19 during the school term, benefits are limited to the two months following the month age 19 is attained. These benefits will be terminated earlier if the student marries, graduates or ceases full-time attendance. An unmarried disabled child over age 18 may qualify if the child became totally disabled before age 22. An unmarried dependent grandchild meeting any of the requirements described above for a child may also qualify if both the grandchild’s parents are deceased or found disabled by the Social Security Administration.
Monthly survivor benefits are also payable to a parent at age 60 who was dependent on the employee for at least half of the parent’s support. If the employee was also survived by a widow(er), surviving divorced spouse or child who could ever qualify for an annuity, the parent’s annuity is limited to the amount that Social Security would pay (Tier I).
- How are Railroad Retirement widow(er)s’ benefits computed?
The Tier I amount of a two-tier survivor benefit is based on the deceased employee’s combined Railroad Retirement and Social Security earnings credits, and is computed using Social Security formulas. In general, the survivor Tier I amount is equal to the amount of survivor benefits that would have been payable under Social Security.
In December 2001, legislation established an “initial minimum amount” which yields, in effect, a widow(er)’s Tier II benefit equal to the Tier II benefit the employee would have received at the time of the award of the widow(er)’s annuity, minus any applicable age reduction.
However, such a Tier II benefit will not receive annual cost-of-living increases until such time as the widow(er)’s annuity, as computed under prior law with all interim cost-of-living increases otherwise payable, exceeds the widow(er)’s annuity as computed under the initial minimum amount formula.
A widow(er) who received a spouse annuity from the RRB is guaranteed that the amount of any widow(er)’s benefit payable will never be less than the annuity she or he was receiving as a spouse in the month before the employee died.
The average annuity awarded to widow(er)s in fiscal year 2020, excluding remarried widow(er)s and surviving divorced spouses, was $2,333 a month. Children received $1,549 a month, on average. Total family benefits for widow(er)s with children averaged $4,395 a month. The average annuity awarded to remarried widow(er)s or surviving divorced spouses in fiscal year 2020 was $1,301 a month.
- Are survivor benefits subject to any reduction for early retirement or disability retirement?
A widow(er), surviving divorced spouse or remarried widow(er) whose annuity begins at full retirement age or later receives the full Tier I amount unless the deceased employee received an annuity that was reduced for early retirement. The eligibility age for a full widow(er)’s annuity is gradually rising to age 67 for those born in 1962 or later, the same as under Social Security. The maximum age reduction is also rising to 20.36%, depending on the widow(er)’s date of birth. For a surviving divorced spouse or remarried widow(er), the maximum age reduction is 28.5%. For a disabled widow(er), disabled surviving divorced spouse or disabled remarried widow(er), the maximum reduction is also 28.5%, even if the annuity begins at age 50.
- Are these benefits subject to offset for the receipt of other benefits?
Under the Railroad Retirement Act, the Tier I portion of a survivor annuity is subject to reduction if any Social Security benefits are also payable, even if the Social Security benefit is based on the survivor’s own earnings. This reduction follows the principles of Social Security law which, in effect, limit payment to the highest of any two or more benefits payable to an individual at one time.
The Tier I portion of a widow(er)’s annuity may also be reduced for the receipt of certain federal, state or local government pension based on the widow(er)’s own earnings. The reduction generally does not apply if the employment on which the public pension is based was covered under the Social Security Act throughout the last 60 months of public employment. However, most military service pensions and payments from the Department of Veterans Affairs will not cause a reduction. Pensions paid by a foreign government or interstate instrumentality will also not cause a reduction.
For those subject to the public pension reduction, the Tier I reduction is equal to 2/3 of the amount of the public pension.
A survivor annuitant should notify the RRB promptly if she or he becomes entitled to any such benefits.
- What if a widow(er) was also a railroad employee and is eligible for a Railroad Retirement employee annuity as well as monthly survivor benefits?
If the widow(er) is entitled to a Railroad Retirement employee annuity and neither the widow(er) nor the deceased employee had any railroad service before 1975, the survivor annuity (Tier I and Tier II) payable to the widow(er) is reduced by the total amount of the widow(er)’s own employee annuity.
If a widow or dependent widower is also a railroad employee annuitant, and either the widow(er) or the deceased employee had at least 120 months of railroad service before 1975, the Tier I reduction may, under certain circumstances, be partially restored in the survivor Tier II amount.
If either the deceased employee or the widow(er) had some railroad service before 1975 but less than 120 months of service, the widow(er)’s own employee annuity and the Tier II portion of the survivor annuity would be payable to the widow(er). The Tier I portion of the survivor annuity would be payable only to the extent that it exceeds the Tier I portion of the widow(er)’s own employee annuity.
- What types of lump-sum death benefits are payable under the Railroad Retirement Act?
A lump-sum death benefit is payable to certain survivors of an employee with 10 or more years of railroad service, or less than 10 years if at least five years were after 1995, and had a current connection with the railroad industry if there is no survivor immediately eligible for a monthly annuity upon the employee’s death.
If the employee did not have 10 years of service before 1975, the lump sum is limited to $255 and is payable only to the widow(er) living in the same household as the employee at the time of the employee’s death.
If the employee had less than 10 years of service but had five years after 1995, he or she must have met Social Security’s insured status requirements for the lump sum to be payable.
If the employee had 10 years of service before 1975, the lump sum is payable to the living-with widow(er). If there is no such widow(er), the lump sum may be paid to the funeral home or the payer of the funeral expenses. These lump sums averaged $1,030 in fiscal year 2020.
If a widow(er) is eligible for monthly benefits at the time of the employee’s death, but the widow(er) had excess earnings deductions which prevented annuity payments or for any other reason did not receive monthly benefits in the 12-month period beginning with the month of the employee’s death totaling at least as much as the lump sum, the difference between the lump-sum benefit and monthly benefits actually paid, if any, is payable in the form of a deferred lump-sum benefit.
The average for all types of lump sums was $933 in fiscal year 2020.
The Railroad Retirement system also provides, under certain conditions, a residual lump-sum death benefit which ensures that a railroad family receives at least as much in benefits as the employee paid in Railroad Retirement taxes before 1975. This benefit is, in effect, a refund of an employee’s pre-1975 Railroad Retirement taxes, after subtraction of any benefits previously paid on the basis of the employee’s service. This benefit is seldom payable.
- How does a person get an estimate of, or apply for, survivor benefits?
As all of the RRB’s 53 field offices are physically closed to the public until further notice because of the COVID-19 pandemic, the best way to obtain a survivor’s annuity estimate is to call the agency’s toll-free number (1-877-772-5772).
Under normal circumstances, applications for survivor benefits are generally filed at one of the RRB’s field offices, with an RRB representative at one of the office’s Customer OutReach Program (CORP) service locations, or by telephone and mail; however, while RRB field offices remain physically closed, applications can be filed solely by telephone and mail by first calling 1-877-772-5772. It is important to note that callers may experience lengthy wait times due to increased call volume caused by COVID-19-related issues.
Notice from John Bragg, the RRB labor member
Brothers and Sisters,
John Bragg
It is hard to believe that 2020 is in the rearview mirror and we are already approaching the mid-point of 2021. The Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) is still operating in a remote capacity with field offices closed to the public. Hopefully, in the not too distant future, I will be writing to advise you of plans for getting back to normal operations. Today, however, I am writing to share a friendly reminder with you about action which every active employee should take on an annual basis – and may be of particular importance this year to some, in light of the unique work circumstances many encountered.
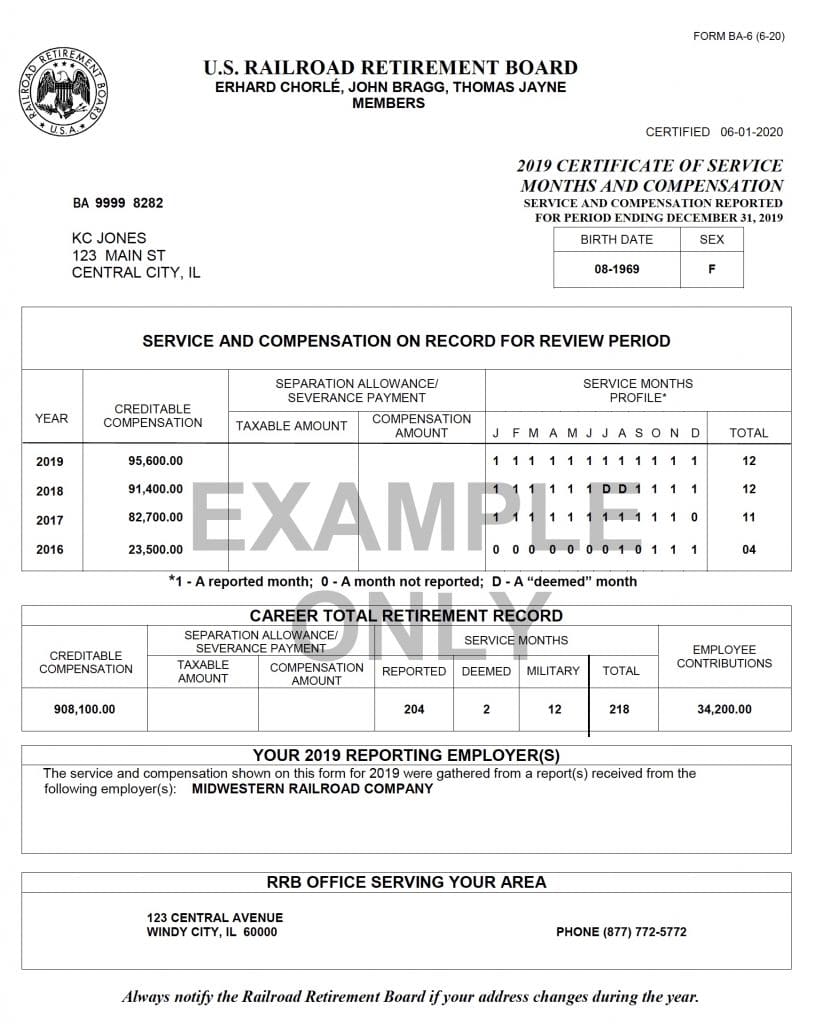
Each year, on or before the last day of February, employers must report service and compensation for each employee who performed compensated service in the preceding calendar year. The RRB, in turn, credits the service and compensation records of individual employees based upon these reports and in June of every year, the RRB releases Form BA-6 to each employee for which compensated service for the preceding year was reported. The Form BA-6 contains the information recently reported for the preceding year, as well as the information reported for three preceding years. For example, the Forms BA-6 which will be released by the RRB in mid-June of 2021 will contain service and compensation reported for the years 2017 through 2020. Regardless of the amount earned, the amount of compensation shown on the Form BA-6 will always be limited by the maximum creditable Tier I compensation amount for the calendar year. For calendar years 2017 through 2020, the maximum amounts creditable are $127,200, $128,400, $132,900 and $137,700, respectively. In addition to showing the creditable compensation for the years 2017 through 2020, the Form BA-6 issued in mid-June of 2021 will show the months for which the employer reported railroad service for the employee during the years 2017-2020.
It is critical that individual employees review their annual Forms BA-6 to make sure that all the information contained on the form is accurate. For example, in addition to validating the creditable compensation, it is important to check to see if the employer properly reported the months for which credit was given by the employer for a month of railroad service. Every month for which you believe you should have credit for railroad service should be coded with a “1”. If the code is “0”, you will not receive credit for any railroad service for that month. If the code is “D” then you will receive credit for railroad service pursuant to the rules governing the deeming of service months.
Employees who received pay for time lost, especially as a result of arbitration proceedings, during the years 2017 through 2020 are reminded of the importance of checking their Forms BA-6. RRB regulations at 20 C.F.R. § 209.15(b) provide that compensation which is pay for time lost must be reported with respect to the year in which the time and compensation were lost. However, it is not uncommon for the individuals responsible for completing reports of service and compensation to be unfamiliar with how to report pay for time lost, or to lack awareness that the compensation they are reporting reflects pay for time lost. As a result, the compensation is mistakenly reported for the year paid AND the service months for which the time and compensation were lost are not credited as railroad service months. Situations where this is most likely to occur are arbitration decisions resulting in the employee being reinstated with all rights and benefits unimpaired and receiving compensation for lost time.
REMEMBER: The law limits the period during which corrections to service and compensation records may be filed to four years from the date the report was due at the RRB, so it is very important for employees to request a correction within that period of time. Any railroad employee who thinks that the Form BA-6 contains an error should be certain to follow the directions on how to file with the RRB a protest of the information contained on the Form BA-6.
RRB Labor Member Press Release:
John Bragg
The Office of the Labor Member is pleased to announce that our 2021 pre-retirement seminar presentation is now available to view online. We designed this program to help educate those nearing retirement about the benefits available to them, and what they can expect during the application process.
This popular program has become a critical resource to RRB customers and employees alike. It helps promote a better understanding of our benefit programs among the railroad community, and in turn, improves the effectiveness of our benefit program operations.
While we typically conduct several seminars across the country annually, we are currently unable to hold in-person events because of COVID-19.
To access the video online, visit RRB.gov/PRS and click on View Pre-Retirement Seminar Presentation. Because we cover several aspects of Railroad Retirement benefits in great detail, the entire presentation is over an hour long. View shorter segments of the program by selecting a seminar topic on the same web page. Available topics include: Retired Employee and Spouse Benefits, Spouse Annuities, Working After Retirement, Survivor Benefits, and Items Affecting All Retirement and Survivor Benefits.

1. How are dual benefits paid to persons entitled to both Railroad Retirement and Social Security benefits?
If a Railroad Retirement annuitant is also awarded a Social Security benefit, the Social Security Administration determines the amount of the Social Security benefit due, but a combined monthly dual benefit payment should, in most cases, be issued by the RRB after the Railroad Retirement annuity has been reduced by the amount of the Social Security benefit.
2. Why is a Railroad Retirement annuity reduced when a Social Security benefit is also payable?
The Tier I portion of a Railroad Retirement annuity is based on both the Railroad Retirement and Social Security earnings credits acquired by an employee and computed under Social Security formulas. It approximates what Social Security would pay if railroad work were covered by Social Security. Tier I benefits are, therefore, reduced by the amount of any actual Social Security benefit paid on the basis of nonrailroad employment, in order to prevent a duplication of benefits based on Social Security-covered earnings.
In addition, following principles of Social Security law which limit payment to the higher of any two or more benefits payable to an individual at one time, the Tier I dual benefit reduction applies to an annuity even if the Social Security benefit is based on the earnings record of someone other than the railroad employee, such as a spouse or former spouse. An annuitant is required to advise the RRB if any benefits are received directly from the Social Security Administration or if those benefits increase (other than for a cost-of-living increase) to avoid a Railroad Retirement benefit overpayment.
The Tier II portion of a Railroad Retirement annuity is based on the railroad employee’s railroad service and earnings alone and is computed under a separate formula. It is not reduced for entitlement to a Social Security benefit.
3. Are there any exceptions to the Railroad Retirement annuity reduction for Social Security benefits?
No. There are no exceptions to the Railroad Retirement annuity reduction for Social Security benefits.
4. Can federal, state or local government pensions also result in dual benefit reductions in an employee’s Railroad Retirement annuity?
Yes. Tier I benefits for employees first eligible for a Railroad Retirement annuity and a federal, state or local government pension after 1985 may be reduced for receipt of a public pension based, in part or in whole, on employment not covered by Social Security or Railroad Retirement after 1956. This may also apply to certain other payments not covered by Railroad Retirement or Social Security, such as payments from a non-profit organization or a foreign government or a foreign employer. Usually, an employee’s Tier I benefit will not be reduced by more than 1/2 of his or her pension from noncovered employment. However, if the employee is under age 65 and receiving a disability annuity, the Tier I benefit may be reduced by an added amount if the pension from noncovered employment is a public disability benefit.
Military service pensions, payments by the Department of Veterans Affairs, or certain benefits payable by a foreign government as a result of a totalization agreement between that government and the United States will not cause a reduction.
5. Can the public service pension reduction apply to spouse or widow(er)s’ benefits?
Yes. The Tier I portion of a spouse’s or widow(er)’s annuity may be reduced for receipt of any federal, state or local government pension separately payable to the spouse or widow(er) based on her or his own earnings. For spouses and widow(er)s subject to a public service pension reduction, the Tier I reduction is equal to 2/3 of the amount of the public service pension.
The reduction generally does not apply if the employment on which the public service pension is based was covered under the Social Security Act throughout the last 60 months of public employment. Most military service pensions and payments from the Department of Veterans Affairs will not cause a reduction. Pensions paid by a foreign government or interstate instrumentality will also not cause a reduction.
6. What dual benefit restrictions apply when both persons in a marriage are railroad employees entitled to Railroad Retirement annuities?
If both parties started railroad employment after 1974, the amount of any spouse or divorced spouse annuity is reduced by the amount of the employee annuity to which the spouse or divorced spouse is also entitled.
If either party had some railroad service before 1975, the spouse or divorced spouse Tier I amount is reduced by the amount of the railroad employee Tier I to which the spouse or divorced spouse is entitled. The spouse or divorced spouse Tier I amount cannot be reduced below zero. The initial reduction is restored in the spouse Tier II amount. Divorced spouses are not entitled to a Tier II component and are not eligible to have the reduction restored.
In survivor cases, if the widow(er) is entitled to a Railroad Retirement employee annuity and neither the widow(er) nor the deceased employee had any railroad service before 1975, the survivor annuity (Tier I and Tier II) payable to the widow(er) is reduced by the total amount of the widow(er)’s own employee annuity.
If a widow or dependent widower is also a railroad employee annuitant, and either the widow(er) or the deceased employee had 120 months of railroad service before 1975, the Tier I reduction may be partially restored in the survivor Tier II amount.
If either the deceased employee or the widow(er) had some railroad service before 1975 but less than 120 months of service, the widow(er)’s own employee annuity and the Tier II portion of the survivor annuity would be payable to the widow(er). The Tier I portion of the survivor annuity would be payable only to the extent that it exceeds the Tier I portion of the widow(er)’s own employee annuity.
7. Can workers’ compensation or public disability benefits affect Railroad Retirement benefits?
If an employee is receiving a Railroad Retirement disability annuity, Tier I benefits for the employee and spouse may, under certain circumstances, be reduced for receipt of workers’ compensation or public disability benefits.
8. How can an annuitant find out if the receipt of any dual benefits affects his or her Railroad Retirement annuity?
If an annuitant becomes entitled to any of the dual benefit payments discussed above, or if there is any question as to whether a dual benefit payment requires a reduction in an annuity, he or she should contact an RRB field office online or by phone. As all of the RRB’s 53 field offices are physically closed to the public until further notice because of the COVID-19 pandemic, customers are encouraged to contact their local office by accessing Field Office Locator at RRB.gov and clicking on Send a Secure Message at the bottom of their local office’s page. Customers who prefer talking to an RRB employee can call the agency’s toll-free number (1-877-772-5772); however, they may experience lengthy wait times due to increased call volume caused by COVID-19-related issues.

The following questions and answers show the differences in Railroad Retirement and Social Security benefits payable at the close of the fiscal year ending Sept. 30, 2020. They also show the differences in age requirements and payroll taxes under the two systems.
1. How do the average monthly Railroad Retirement and Social Security benefits paid to retired employees and spouses compare?
The average age annuity being paid by the Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) at the end of fiscal year 2020 to career rail employees was $3,735 a month, and for all retired rail employees the average was $2,985. The average age retirement benefit being paid under Social Security was approximately $1,505 a month. Spouse benefits averaged $1,090 a month under Railroad Retirement compared to $765 under Social Security.
The Railroad Retirement Act also provides supplemental Railroad Retirement annuities of between $23 and $43 a month, which are payable to employees with railroad service prior to October 1981 who retire directly from the rail industry with 25 or more years of service.
2. Are the benefits awarded to recent retirees generally greater than the benefits payable to those who retired years ago?
Yes, because recent awards are based on higher average earnings. Age annuities awarded to career railroad employees retiring in fiscal year 2020 averaged about $4,370 a month while monthly benefits awarded to workers retiring at full retirement age under Social Security averaged nearly $2,070. If spouse benefits are added, the combined benefits for the employee and spouse would total $6,115 under Railroad Retirement coverage, compared to $3,105 under Social Security. Adding a supplemental annuity to the railroad family’s benefit increases average total benefits for current career rail retirees to about $6,135 a month.
3. How much are the disability benefits currently awarded?
Disabled railroad workers retiring directly from the railroad industry in fiscal year 2020 were awarded $3,160 a month on average while awards for disabled workers under Social Security averaged $1,415.
While both the Railroad Retirement and Social Security Acts provide benefits to workers who are totally disabled for any regular work, the Railroad Retirement Act also provides disability benefits specifically for employees who are disabled for work in their regular railroad occupation. Employees may be eligible for such an occupational disability annuity at age 60 with 10 years of service, or at any age with 20 years of service.
4. Can railroaders receive benefits at earlier ages than workers under Social Security?
Railroad employees with 30 or more years of creditable service are eligible for regular annuities based on age and service the first full month they are age 60, and rail employees with less than 30 years of creditable service are eligible for regular annuities based on age and service the first full month they are age 62.
No early retirement reduction applies if a rail employee retires at age 60 or older with 30 years of service and his or her retirement is after 2001, or if the employee retired before 2002 at age 62 or older with 30 years of service.
Early retirement reductions are otherwise applied to annuities awarded before full retirement age (the age at which an employee can receive full benefits with no reduction for early retirement). Full retirement age is age 66 for those born 1943 through 1954 and is gradually rising to age 67 for those born in 1960 or later, the same as under Social Security.
Under Social Security, a worker cannot begin receiving retirement benefits based on age until age 62, regardless of how long he or she worked, and Social Security retirement benefits are reduced for retirement prior to full retirement age regardless of years of coverage.
5. Can the spouse of a railroader receive a benefit at an earlier age than the spouse of a worker under Social Security?
If a retired railroad employee with 30 or more years of service is age 60, the employee’s spouse is also eligible for an annuity the first full month the spouse is age 60. The spouse of a worker under Social Security is not eligible for a spouse benefit based on age until both the worker and the spouse are at least age 62. Regardless of age, the spouses of workers under both retirement systems are eligible if the worker is retired and the spouse is caring for a qualifying child.
6. Does Social Security offer any benefits that are not available under Railroad Retirement?
Social Security does pay certain types of benefits that are not available under Railroad Retirement. For example, Social Security provides children’s benefits when an employee is disabled, retired or deceased, whereas the RRB only pays children’s benefits if the employee is deceased.
However, the Railroad Retirement Act includes a special minimum guaranty provision, which ensures that railroad families will not receive less in monthly benefits than they would have if railroad earnings were covered by Social Security rather than Railroad Retirement laws. This guaranty is intended to cover situations in which one or more members of a family would otherwise be eligible for a type of Social Security benefit that is not provided under the Railroad Retirement Act. Therefore, if a retired rail employee has children who would otherwise be eligible for a benefit under Social Security, the employee’s annuity can be increased to reflect what Social Security would pay the family.
7. How much are monthly benefits for survivors under Railroad Retirement and Social Security?
Survivor benefits are generally higher if payable by the RRB rather than Social Security. At the end of fiscal year 2020, the average annuity being paid to all aged and disabled widow(er)s was $1,825 a month, compared to $1,380 under Social Security.
Benefits awarded by the RRB in fiscal year 2020 to aged and disabled widow(er)s of railroaders averaged about $2,340 a month, compared to approximately $1,355 under Social Security.
The annuities being paid at the end of fiscal year 2020 to widowed mothers/fathers averaged $1,990 a month and children’s annuities averaged $1,195, compared to $1,030 and $900 a month for widowed mothers/fathers and children, respectively, under Social Security.
Those awarded in fiscal year 2020 averaged $1,780 a month for widowed mothers/fathers and $1,545 a month for children under Railroad Retirement, compared to $1,015 and $905 for widowed mothers/fathers and children, respectively, under Social Security.
8. How do Railroad Retirement and Social Security lump-sum death benefit provisions differ?
Both the Railroad Retirement and Social Security systems provide a lump-sum death benefit. The Railroad Retirement lump-sum benefit is generally payable only if survivor annuities are not immediately due upon an employee’s death. The Social Security lump-sum benefit may be payable regardless of whether monthly benefits are also due. Both Railroad Retirement and Social Security provide a lump-sum benefit of $255. However, if a railroad employee completed 10 years of creditable railroad service before 1975, the average Railroad Retirement lump-sum benefit payable is $1,030. Also, if an employee had less than 10 years of service, but had at least 5 years of such service after 1995, he or she would have to have had an insured status under Social Security law (counting both Railroad Retirement and Social Security credits) in order for the $255 lump-sum benefit to be payable.
The Social Security lump sum is generally only payable to the widow(er) living with the employee at the time of death. Under Railroad Retirement, if the employee had 10 years of service before 1975, and was not survived by a living-with widow(er), the lump sum may be paid to the funeral home or the payer of the funeral expenses.
9. How do Railroad Retirement and Social Security payroll taxes compare?
Railroad Retirement payroll taxes, like Railroad Retirement benefits, are calculated on a two-tier basis. Rail employees and employers pay Tier I taxes at the same rate as Social Security taxes, 7.65%, consisting of 6.20% for retirement on earnings up to $142,800 in 2021, and 1.45% for Medicare hospital insurance on all earnings. An additional 0.9% in Medicare taxes (2.35% in total) will be withheld from employees on earnings above $200,000.
In addition, rail employees and employers both pay Tier II taxes, which are used to finance Railroad Retirement benefit payments over and above Social Security levels. In 2021, the Tier II tax rate on earnings up to $106,200 is 4.9% for employees and 13.1% for employers.
10. How much are regular Railroad Retirement taxes for an employee earning $142,800 in 2021 compared to Social Security taxes?
The maximum amount of regular Railroad Retirement taxes that an employee earning $142,800 can pay in 2021 is $16,128, compared to $10,924.20 under Social Security. For railroad employers, the maximum annual regular retirement taxes on an employee earning $142,800 are $24,836.40, compared to $10,924.20 under Social Security. Employees earning over $142,800 and their employers will pay more in retirement taxes than the above amounts because the Medicare hospital insurance tax is applied to all earnings.