
OSHA and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) are working together on a public education effort aimed at improving the way people prepare for and respond to severe weather.
Cold stress
It is important for employers to know the wind chill temperature so that they can gauge workers’ exposure
The NOAA Weather Radio is a nationwide network of radio stations broadcasting continuous weather information from the nearest NWS office. It will give information when wind chill conditions reach critical thresholds. A Wind Chill Warning is issued when wind chill temperatures are life-threatening. A Wind Chill Advisory is issued when wind chill temperatures are potentially hazardous.
Who is affected by environmental cold?
Risk factors for cold stress include:
- Wetness/dampness, dressing improperly and exhaustion
- Predisposing health conditions such as hypertension, hypothyroidism and diabetes
- Poor physical conditioning
What constitutes cold stress and its effects can vary across different areas of the country. In regions that are not used to winter weather, near freezing temperatures are considered factors for “cold stress.” Increased wind speed also causes heat to leave the body more rapidly (wind chill effect). Wetness or dampness, even from body sweat, also facilitates heat loss from the body. Cold stress occurs by driving down the skin temperature, and eventually the internal body temperature. When the body is unable to warm itself, serious cold-related illnesses and injuries may occur, and permanent tissue damage and death may result. Types of cold stress include: trench foot, frostbite and hypothermia.
For more information, see OSHA’s Cold Stress Safety and Health Guide.
Trench foot is a non-freezing injury of the feet caused by prolonged exposure to wet and cold conditions. It can occur in temperatures as high as 60°F if feet are constantly wet. Injury occurs because wet feet lose heat 25-times faster than dry feet.
What are they symptoms of trench foot?
Reddening skin, tingling, pain, swelling, leg cramps, numbness and blisters.
First Aid
- Call 911 immediately in an emergency; otherwise seek medical assistance as soon as possible.
- Remove wet shoes/boots and wet socks.
- Dry the feet and avoid working on them.
- Keep affected feet elevated and avoid walking. Get medical attention.
Frostbite is caused by the freezing of the skin and tissues. Frostbite can cause permanent damage to the body, and in severe cases can lead to amputation. The risk of frostbite is increased in people with reduced blood circulation and among people who are not dressed properly for extremely cold temperatures.
What are the symptoms of frostbite?
Reddened skin develops gray/white patches in the fingers, toes, nose, or ear lobes; tingling, aching, a loss of feeling, firm/hard, and blisters may occur in the affected areas.
First Aid
- Follow the recommendations described below for hypothermia.
- Protect the frostbitten area, e.g., by wrapping loosely in a dry cloth and protect the area from contact until medical help arrives.
- DO NOT rub the affected area, because rubbing causes damage to the skin and tissue.
- Do not apply snow or water. Do not break blisters.
- DO NOT try to re-warm the frostbitten area before getting medical help, for example, do not use heating pads or place in warm water. If a frostbitten area is rewarmed and gets frozen again, more tissue damage will occur. It is safer for the frostbitten area to be rewarmed by medical professionals.
- Give warm sweetened drinks if alert (no alcohol).
Hypothermia occurs when the normal body temperature (98.6°F) drops to less than 95°F. Exposure to cold temperatures causes the body to lose heat faster than it can be produced. Prolonged exposure to cold will eventually use up the body’s stored energy. The result is hypothermia, or abnormally low body temperature. Hypothermia is most likely at very cold temperatures, but it can occur even at cool temperatures (above 40°F) if a person becomes chilled from rain, sweat, or immersion in cold water.
What are the symptoms of hypothermia?
An important mild symptom of hypothermia is uncontrollable shivering, which should not be ignored. Although shivering indicates that the body is losing heat, it also helps the body to rewarm itself. Moderate to severe symptoms of hypothermia are loss of coordination, confusion, slurred speech, heart rate/breathing slow, unconsciousness and possibly death. Body temperature that is too low affects the brain, making the victim unable to think clearly or move well. This makes hypothermia particularly dangerous because a person may not know what is happening and won’t be able to do anything about it.
First Aid
- Call 911 immediately in an emergency.
- Move the worker to a warm, dry area.
- Remove any wet clothing and replace with dry clothing. Wrap the entire body (including the head and neck) in layers of blankets; and with a vapor barrier (e.g. tarp, garbage bag) Do not cover the face.
If medical help is more than 30 minutes away:
- Give warm sweetened drinks if alert (no alcohol), to help increase the body temperature. Never try to give a drink to an unconscious person.
- Place warm bottles or hot packs in armpits, sides of chest, and groin. Call 911 for additional rewarming instructions.
Co-workers trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) may help a person suffering from hypothermia who has no pulse or is not breathing:
- Call 911 for emergency medical assistance immediately.
- Treat the worker as per instructions for hypothermia, but be very careful and do not try to give an unconscious person fluids.
- Check him/her for signs of breathing and for a pulse. Check for 60 seconds.
- If after 60 seconds the affected worker is not breathing and does not have a pulse, trained workers may start rescue breaths for 3 minutes.
- Recheck for breathing and pulse, check for 60 seconds.
- If the worker is still not breathing and has no pulse, continue rescue breathing.
- Only start chest compressions per the direction of the 911 operator or emergency medical services*
- Reassess patient’s physical status periodically.
*Chest compressions are recommended only if the patient will not receive medical care within 3 hours.
Wind Chill Temperature
Outdoor workers exposed to cold and windy conditions are at risk of cold stress, both air temperature and wind speed affect how cold they feel. “Wind chill” is the term used to describe the rate of heat loss from the human body, resulting from the combined effect of low air temperature, and wind speed. The wind chill temperature is a single value that takes both air temperature and wind speed into account. For example, when the air temperature is 40°F, and the wind speed is 35mph, the wind chill temperature is 28°F; this measurement is the actual effect of the environmental cold on the exposed skin.
National Weather Service (NWS) Wind Chill Calculator: With this tool, one may input the air temperature and wind speed, and it will calculate the wind chill temperature.
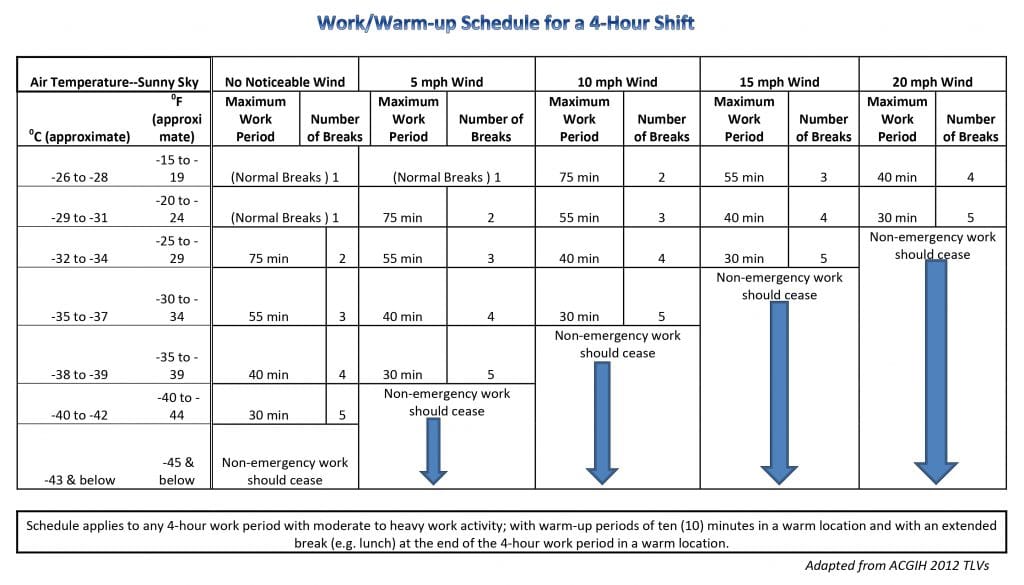
The American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) developed the following Work/Warm-up Schedule for a 4-hour shift that takes both air temperature and wind speed into account to provide recommendations on scheduling work breaks and ceasing non-emergency work.
Dressing Properly for the Cold
Dressing properly is extremely important to preventing cold stress. When cold environments or temperatures cannot be avoided, the following would help protect workers from cold stress:
- Wear at least three layers of loose-fitting clothing. Layering provides better insulation.
- An inner layer of wool, silk or synthetic (polypropylene) to keep moisture away from the body. Thermal wear, wool, silk or polypropylene, inner layers of clothing that will hold more body heat than cotton.
- A middle layer of wool or synthetic to provide insulation even when wet.
- An outer wind and rain protection layer that allows some ventilation to prevent overheating.
- Tight clothing reduces blood circulation. Warm blood needs to be circulated to the extremities. Insulated coat/jacket (water resistant if necessary)
- Knit mask to cover face and mouth (if needed)
- Hat that will cover your ears as well. A hat will help keep your whole body warmer. Hats reduce the amount of body heat that escapes from your head.
- Insulated gloves (water resistant if necessary), to protect the hands
- Insulated and waterproof boots to protect the feet
- Your employer should ensure that you know the symptoms of cold stress
- Monitor your physical condition and that of your coworkers
- Dress appropriately for the cold
- Stay dry in the cold because moisture or dampness, e.g. from sweating, can increase the rate of heat loss from the body
- Keep extra clothing (including underwear) handy in case you get wet and need to change
- Drink warm sweetened fluids (no alcohol)
- Use proper engineering controls, safe work practices, and personal protective equipment (PPE) provided by your employer
Winter driving
Although employers cannot control roadway conditions, they can promote safe driving behavior by ensuring workers recognize the hazards of winter weather driving, for example, driving on snow/ice covered roads; are properly trained for driving in winter weather conditions; and are licensed (as applicable) for the vehicles they operate. For information about driving safely during the winter, visit OSHA’s Safe Winter Driving page.
Employers should set and enforce driver safety policies. Employers should also implement an effective maintenance program for all vehicles and mechanized equipment that workers are required to operate. Crashes can be avoided. Learn more at the Motor Vehicle Safety (OSHA Safety and Health Topics Page) .
Employers should ensure properly trained workers inspect the following vehicle systems to determine if they are working properly:
- Brakes: Brakes should provide even and balanced braking. Also check that brake fluid is at the proper level.
- Cooling system: Ensure a proper mixture of 50/50 antifreeze and water in the cooling system at the proper level.
- Electrical system: Check the ignition system and make sure that the battery is fully charged and that the connections are clean. Check that the alternator belt is in good condition with proper tension.
- Engine: Inspect all engine systems.
- Exhaust system: Check exhaust for leaks and that all clamps and hangers are snug.
- Tires: Check for proper tread depth and no signs of damage or uneven wear. Check for proper tire inflation.
- Oil: Check that oil is at proper level.
- Visibility systems: Inspect all exterior lights, defrosters (windshield and rear window), and wipers. Install winter windshield wipers.
An emergency kit with the following items is recommended in vehicles:
- Cell phone or two-way radio
- Windshield ice scraper
- Snow brush
- Flashlight with extra batteries
- Shovel
- Tow chain
- Traction aids (bag of sand or cat litter)
- Emergency flares
- Jumper cables
- Snacks
- Water
- Road maps
- Blankets, change of clothes
Preventing slips on snow and ice
To prevent slips, trips, and falls, employers should clear snow and ice from walking surfaces, and spread deicer as quickly as possible after a winter storm. When walking on snow or ice is unavoidable workers should be trained to:
- Wear footwear that has good traction and insulation (e.g. insulated and water-resistant boots or rubber over-shoes with good rubber treads)
- Take short steps and walk at a slower pace to react quickly to changes in traction
 Anyone working in a cold environment may be at risk of cold stress. Some workers may be required to work outdoors in cold environments and for extended periods, for example, snow cleanup crews, sanitation workers, police officers and emergency response and recovery personnel, like firefighters, and emergency medical technicians. Cold stress can be encountered in these types of work environment. The following frequently asked questions will help workers understand what cold stress is, how it may affect their health and safety, and how it can be prevented.
Anyone working in a cold environment may be at risk of cold stress. Some workers may be required to work outdoors in cold environments and for extended periods, for example, snow cleanup crews, sanitation workers, police officers and emergency response and recovery personnel, like firefighters, and emergency medical technicians. Cold stress can be encountered in these types of work environment. The following frequently asked questions will help workers understand what cold stress is, how it may affect their health and safety, and how it can be prevented.