SMART members, allies submitted 13,000 comments in favor of the regulation
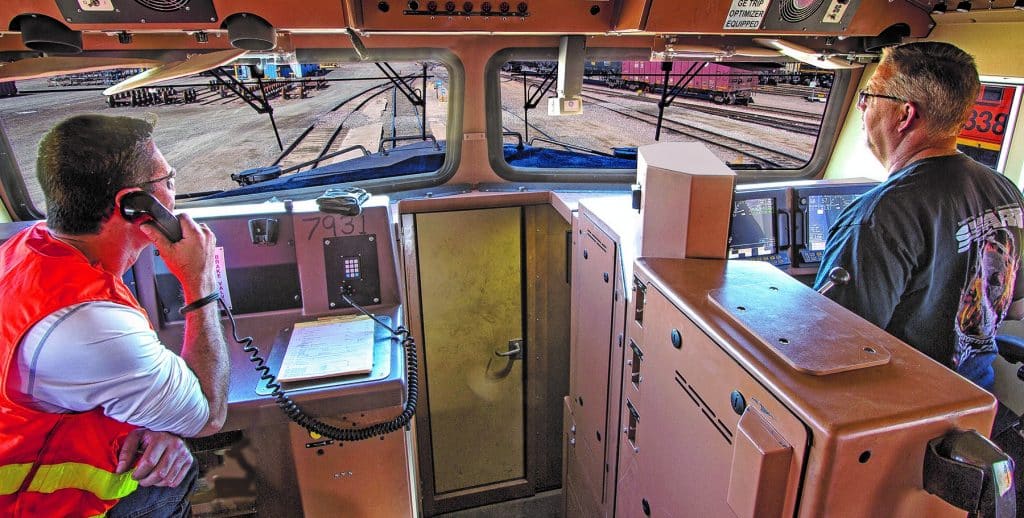
On April 2, 2024, after a yearslong effort by SMART-TD members and leadership, United States Department of Transportation (DOT) Secretary Pete Buttigieg and Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) Administrator Amit Bose announced that there will be a minimum of two certified rail crew members assigned to the cab of freight trains in this country. At long last, a nation-spanning two-person crew regulation has been implemented in the U.S.
The FRA ruling on the Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM), originally released in 2022, finally puts safety first for the railroad industry. And with this action, President Joe Biden’s Department of Transportation delivered on a promise made in 2020, supporting our ongoing struggle to force railroads to responsibly operate their trains.
“Today’s ruling codifying the two-person freight crew not only demonstrates this administration’s dedication to the safety of this country and our workforce, but it also shows their respect and acknowledgment of our men and women and the work they do,” SMART-TD President Jeremy Ferguson said the day the rule was published. “They see our value to this nation’s economy and security. Every railroad professional should take pride in this accomplishment and recognition.”
The finalization of a federal two-person crew regulation comes after a long fight between SMART-TD and the Association of American Railroads (AAR), the companies it represents and the hedge fund operators who own many U.S. railroads. (A little more than a week after the FRA’s announcement, railroads challenged the action in appeals court.)
The decision also represents a sea change in federal railroad policy.
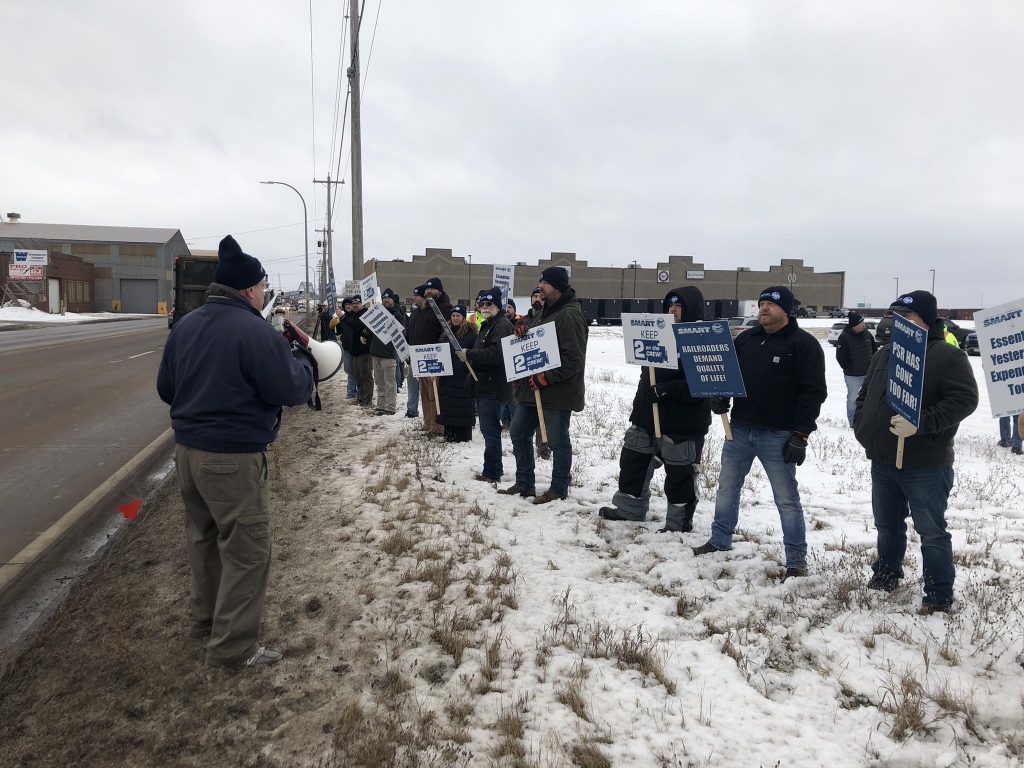

From 2017 to 2020, SMART-TD leaders and members battled against an anti-worker FRA that withdrew a proposed two-person crew regulation and attempted to pre-empt individual state two-person crew laws. In contrast, the current FRA re-proposed federal two-person crew policy, asked for stakeholder input and received it. Secretary Buttigieg and Administrator Bose have both met repeatedly with railroaders and union leadership throughout their respective terms, and they actively encouraged those who are most impacted by railroad policy — the workers who keep the trains moving — to let decision makers know what conditions are like on America’s rail system.
From International leadership to rank-and-file railroaders, our union has done just that, pursuing decisive action in the name of union jobs and rail safety.
“When this rule came open for public comments, SMART members and allies stood up and spoke with over 13,000 responses to the FRA. Today, we all celebrate the result and the essential proof of the value of the labor of the people aboard the nation’s freight trains,” Ferguson continued. “This effort defines what it is to be a union and the power of workers to stand as one. We did it together as a SMART-TD family, and I am unbelievably proud to be the president of this union in what is a defining moment for our industry — a moment when safety finally and deservedly came first.”
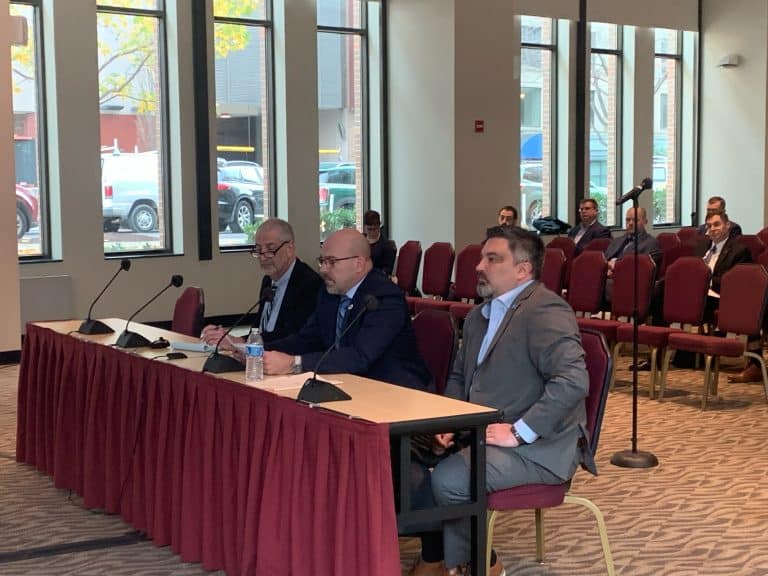

After the rule was put forward by the FRA in 2022, a lengthy public commenting period was initiated — and then extended. Members took advantage with their tens of thousands of comments. And while railroaders were making their voices heard, TD President Ferguson and our union’s national and state legislative officers relentlessly pushed lawmakers and government officials to understand the safety ramifications of a nation with single-person freight train crews. Ferguson attended and testified at the FRA’s public hearing on the regulation in December 2022 and delivered 20 minutes of firsthand accounts to FRA officials, demanding they take this step to protect the country from the railroad companies’ greed.
Meanwhile, SMART-TD National Legislative Director Gregory Hynes and Alternate National Legislative Director Jared Cassity orchestrated outreach to every state in the U.S., mobilizing our members to stand up and take part in the public comment period — resulting in our record-setting number of submissions.
And during nationwide rail labor rallies in winter 2022, SMART-TD members and fellow rail workers sounded the alarm on precision Scheduled railroading, blocked crossings, the need for two-person crews and more, with a Washington, DC, rally drawing dozens of congressional allies.
“It is no secret that the railroads in this country have been relentlessly pursuing a way to cut our rail crews down to one person. They have poured millions of dollars into pursuing technology that allows them to do this,” Cassity said. “These corporations are open with the fact that they see more value in the trajectory of their stock prices than in the safety of this country or the well-being of the conductors and engineers who are the bedrock of our economy. This fight raged for years, and as a union family, we stood toe to toe with the railroads. I want to thank our members for staying engaged in this fight.”
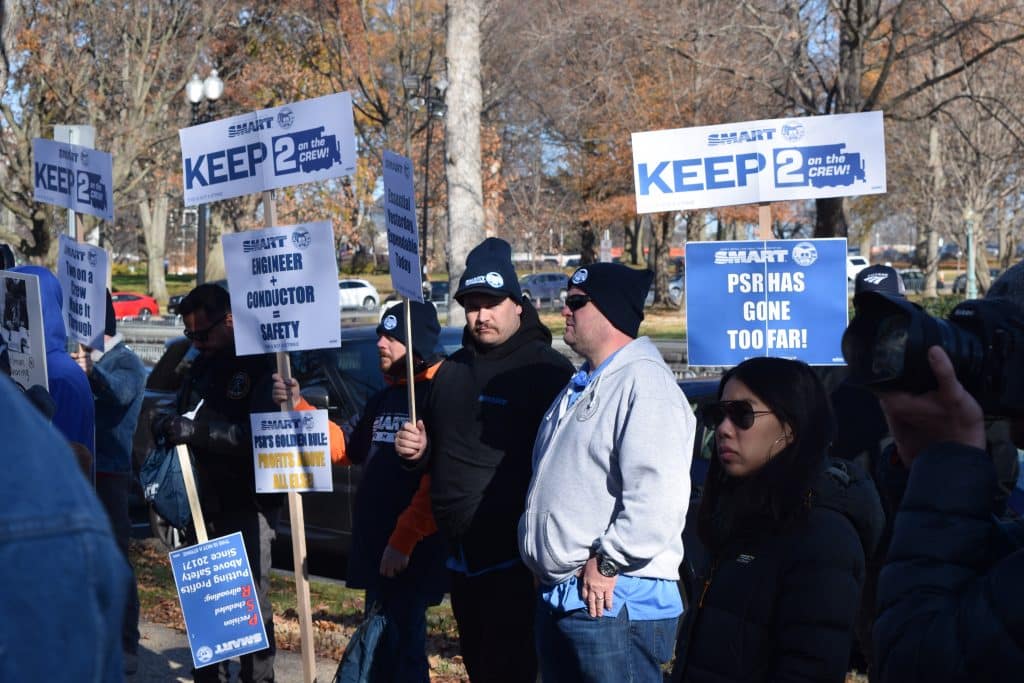
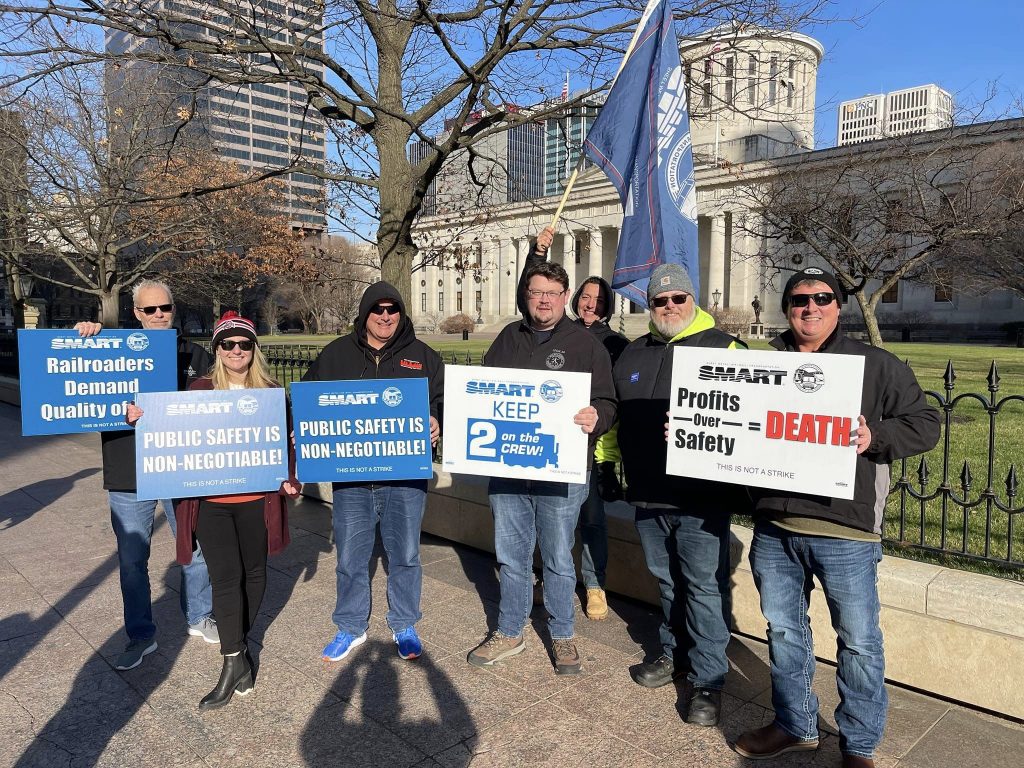




Hynes gave credit for this win to the collective effort of railroad workers and state legislative committees throughout SMART.
“This announcement didn’t come out of thin air. It came from the hard work and dedication of SMART-TD’s men and women!” Hynes said. “Two-person crew regulations have been discussed for years, through multiple presidencies and even more sessions of Congress. The men and women of this union have never relented or allowed this issue to get pushed to the side. Our state legislative directors have taken up this fight state after state. Our members have made their voices heard from coast to coast on this issue. Today, we reach a place where our vigilance and persistence have paid off. This administration got it done.”
The regulation, mired in partisan back-and-forth throughout the rulemaking process, was not a certainty — as demonstrated by the fact that it was announced nearly two years after proposal. During the long wait for federal action, SMART-TD state legislative boards worked unceasingly to get a dozen states to set a minimum crew size, and our work will continue should the regulation change under a future presidential administration.
“We have every right to celebrate this ruling from the Biden administration, but we cannot for one second think this fight is over,” Cassity added. “We must stay informed, involved and on offense. These railroads aren’t used to losing. They will come out swinging to argue against the reality that our people matter, and we have got to be ready for it. SMART-TD remains vigilant, and we ask you to continue to stand with us.”
A brief history of the fight for two-person crews
May 28, 1992: A regulation in Arizona is adopted stating railroads in the state “shall maintain a minimum of two operating employees in the control compartment of the lead locomotive unit of a train.”
May 12, 1993: West Virginia Gov. Gaston Caperton signs a bill amending a 1931 state law. The new law states “no railroad may permit or require any crew controlled locomotive power unit, including helper units, that is not attached to a train to be operated by a crew of fewer than two persons.”
Dec. 15, 1997: A two-person crew state law, the first in the nation, is backed by the United Transportation Union and referred to by Gov. Tommy Thompson as “the UTU bill.” The legislation is signed and implemented in Wisconsin, making it the first to legislate crew size.
March 2000: Wyoming’s Legislature passes a two-person crew bill in the state. It is vetoed by Gov. Jim Geringer.
July 6, 2013: The brakes are disengaged on a train with a single-person crew in Lac-Megantic, Quebec, Canada. The train, carrying crude oil, derails and explodes in the middle of the town, with 47 people losing their lives.
July 23, 2013: Transport Canada bans all single-person crews from trains carrying any amount of hazardous materials in the country.
Aug. 2, 2013: A federal two-person crew size bill, H.R. 3040, which would establish a minimum freight crew size in the U.S., is introduced by initial sponsors Reps. Michael Michaud and Chellie Pingree in the U.S. House. It gains 82 cosponsors before the congressional session’s conclusion.
Aug. 29, 2013: FRA’s Railroad Safety Advisory Committee (RSAC) convenes an emergency working group to examine appropriate freight rail crew sizes.
Spring 2014: SMART Transportation Division and the BLET announce a joint effort, including model bill language, to get legislation passed to maintain two-person crews on the state level.
April 9, 2014: FRA announces its intent to create a rulemaking on train crew staffing in the future.
Sept. 10, 2014: Sens. Richard Blumenthal and Charles Schumer introduce S. 2784, the Rail Safety Improvement Act of 2014 (including a two-person crew provision) in the Senate.
April 13, 2015: U.S. Rep. Don Young introduces the Safe Freight Act (H.R. 1763), which would establish a minimum crew size. It gains 69 cosponsors prior to the session’s conclusion.
Sept. 8, 2015: California Gov. Jerry Brown signs two-person crew legislation.
March 15, 2016: The FRA, under President Obama-appointed Administrator Sarah Feinberg, issues a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) to set a minimum freight crew size and opens comments.
Aug. 15, 2016: Comment period closes on the NPRM. More than 1,500 comments were received in favor of the rule, while 36 were received against.
Jan. 3, 2017: Rep. Young reintroduces the Safe Freight Act (H.R. 233) to establish a minimum crew size. It gains 120 cosponsors. A companion bill is introduced in the Senate by Sen. Heidi Heitkamp of North Dakota and gains 13 cosponsors.
June 8, 2017: Gov. Brian Sandoval of Nevada vetoes a two-person freight crew bill after its passage.
May 25, 2018: Gov. Larry Hogan of Maryland vetoes a two-person freight crew bill after its passage in the state General Assembly.
March 2019: Rep. Young again introduces a version of the Safe Freight Act (H.R. 1748). It gains 141 cosponsors in its lifetime. A companion bill (S. 1979) is introduced in the U.S. Senate by Sen. Edward Markey and gains 15 cosponsors.
March 21, 2019: Colorado Gov. Jared Polis signs two-person crew legislation into law for his state.
May 14, 2019: Nevada Gov. Steve Sisolak signs a two-person crew bill into law.
May 23, 2019: FRA and its Trump-appointed administrator, ex-Conrail CEO Ron Batory, announce the withdrawal of the NPRM from 2016 that sought to set a minimum freight crew size. FRA also declares state two-person crew legislation pre-empted.
July 16, 2019: FRA’s decision to withdraw the crew size NPRM is challenged in court by SMART-TD and multiple states.
Aug. 9, 2019: Defying Batory’s order of pre-emption, Illinois Gov. J.B. Pritzker signs into law a bill requiring two-person crews in his state.
Oct. 30, 2019: Indiana Railroad, a shortline that uses single-person crew operations, sues the state of Illinois over its two-person crew law with the backing of the Association of American Railroads and the American Short Line and Regional Railroad Association, nullifying the law.
June 11, 2020: Washington state’s two-person crew law takes effect. It was signed by Gov. Jay Inslee earlier in the year after nearly seven years in limbo.
July 27, 2020: Gov. Laura Kelly and the Department of Transportation in Kansas announce the state’s intent to establish a minimum crew size. Implementation of this regulation is blocked by the state’s attorney general.
Feb. 23, 2021: After a legal battle, a Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals victory for the union is achieved. The Trump-era FRA’s decision to throw out the crew-size NPRM and the declaration of pre-emption are reversed. The Rule of Two is sent back to the U.S. DOT/FRA for re-evaluation.
June 4, 2021: U.S. Rep. Peter DeFazio introduces the INVEST in America act, which contains a two-person minimum crew size provision that passes the U.S. House. During the reconciliation process with the Senate, the two-person crew element is removed from the bill.
May 31, 2022: A two-person crew bill passes both houses of the New York Legislature, but Gov. Kathy Hochul fails to act on the bill.
July 28, 2022: In response to the court order that remanded the NPRM back to FRA, President Biden’s FRA Administrator Amit Bose reopens the docket and solicitation for public comments on the NPRM.
Dec. 12, 2022: FRA hosts a public hearing regarding the crew size NPRM. TD President Jeremy Ferguson and SMART members provide in-person testimony in support of the Rule of Two.
Dec. 21, 2022: Comment period closes for the crew size NPRM. More than 13,000 comments are received in favor of the rule, with only 64 against.
Feb. 2, 2023: A Norfolk Southern derailment in East Palestine, Ohio, draws attention to matters of railroad safety.
March 1, 2023: The 2023 Railway Safety Act is introduced by U.S. Sens. Sherrod Brown and J.D. Vance of Ohio, which would establish a two-person crew throughout the country, among other safety measures.
March 31, 2023: Ohio Gov. Mike DeWine signs a rail safety bill requiring two-person crews aboard freight trains.
May 2023: Kansas Gov. Laura Kelly and the state Department of Transportation again announce the state’s intent to regulate a minimum crew size.
May 24, 2023: Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz signs a rail safety bill requiring two-person crews aboard freight trains in the state.
June 29, 2023: The Association of American Railroads sues on behalf of the carriers to challenge Ohio’s law.
Oct. 11, 2023: Kansas implements its regulation requiring a minimum train crew size.
Dec. 8, 2023: The New York Legislature passes two-person crew legislation for the second straight year. Given a second opportunity, Gov. Kathy Hochul signs the bill.
March 8, 2024: Virginia Gov. Glenn Youngkin vetoes a two-person crew bill after it was passed by the Legislature.